Glass curtain walls are a transformative feature in modern architecture, combining beauty, functionality, and sustainability. The right choice of materials, design, and installation techniques can lead to a highly efficient, aesthetically pleasing, and durable building façade. For any building project, it’s crucial to choose the appropriate type of curtain wall system to meet both the structural requirements and aesthetic goals.

Point support curtain wall structure diagram
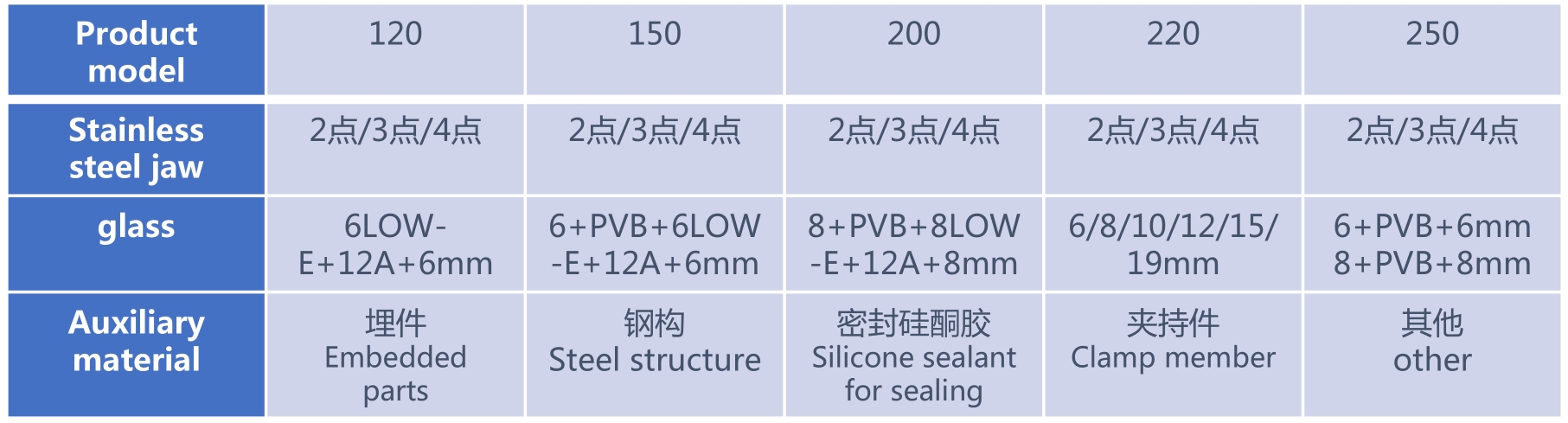
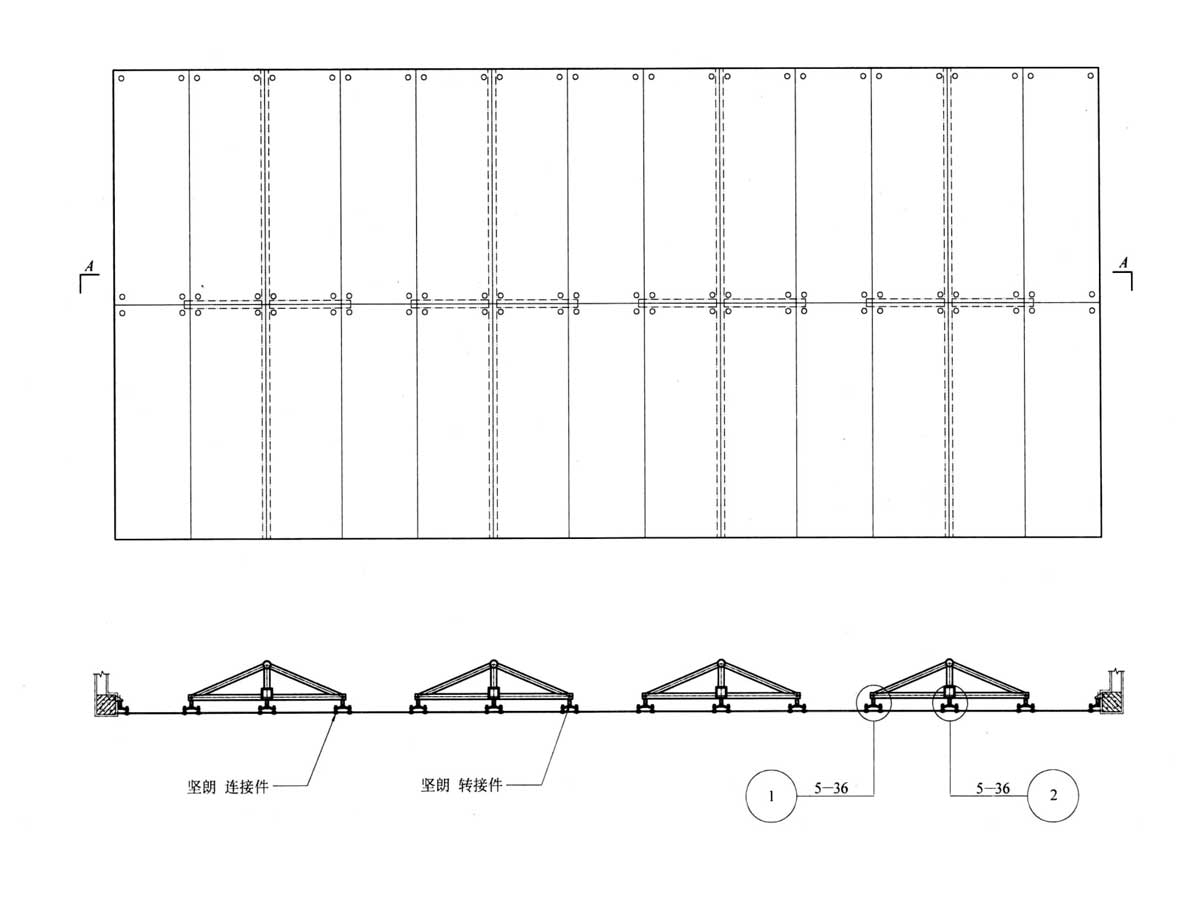
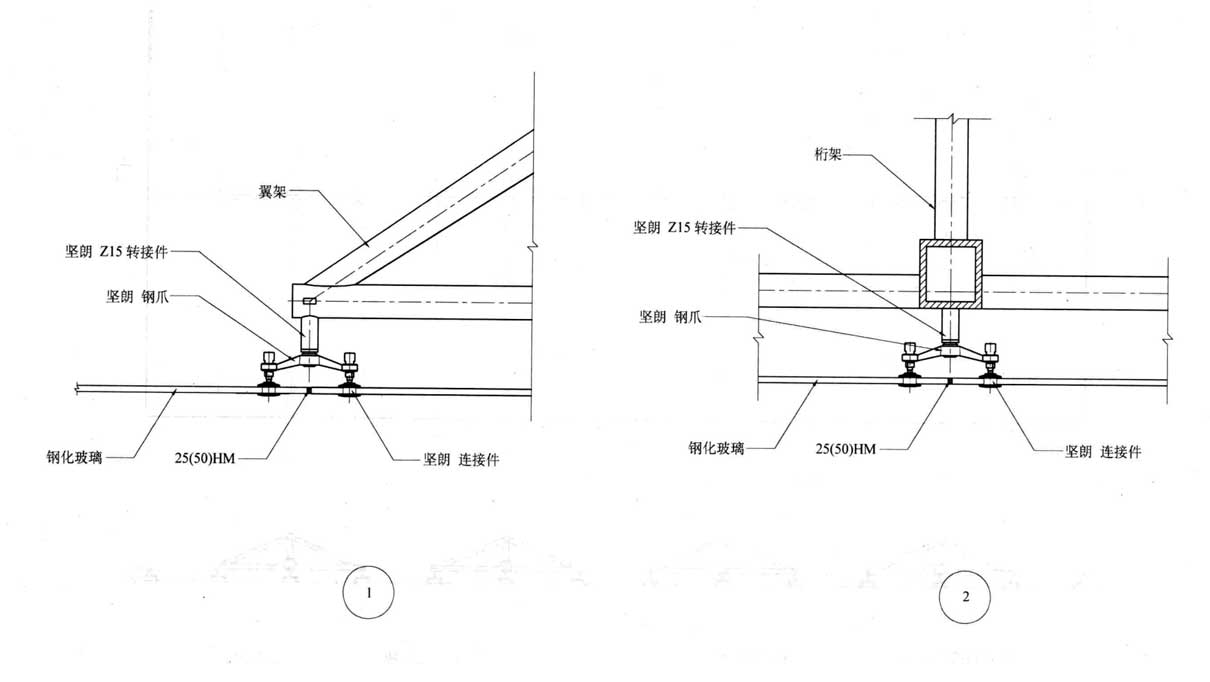
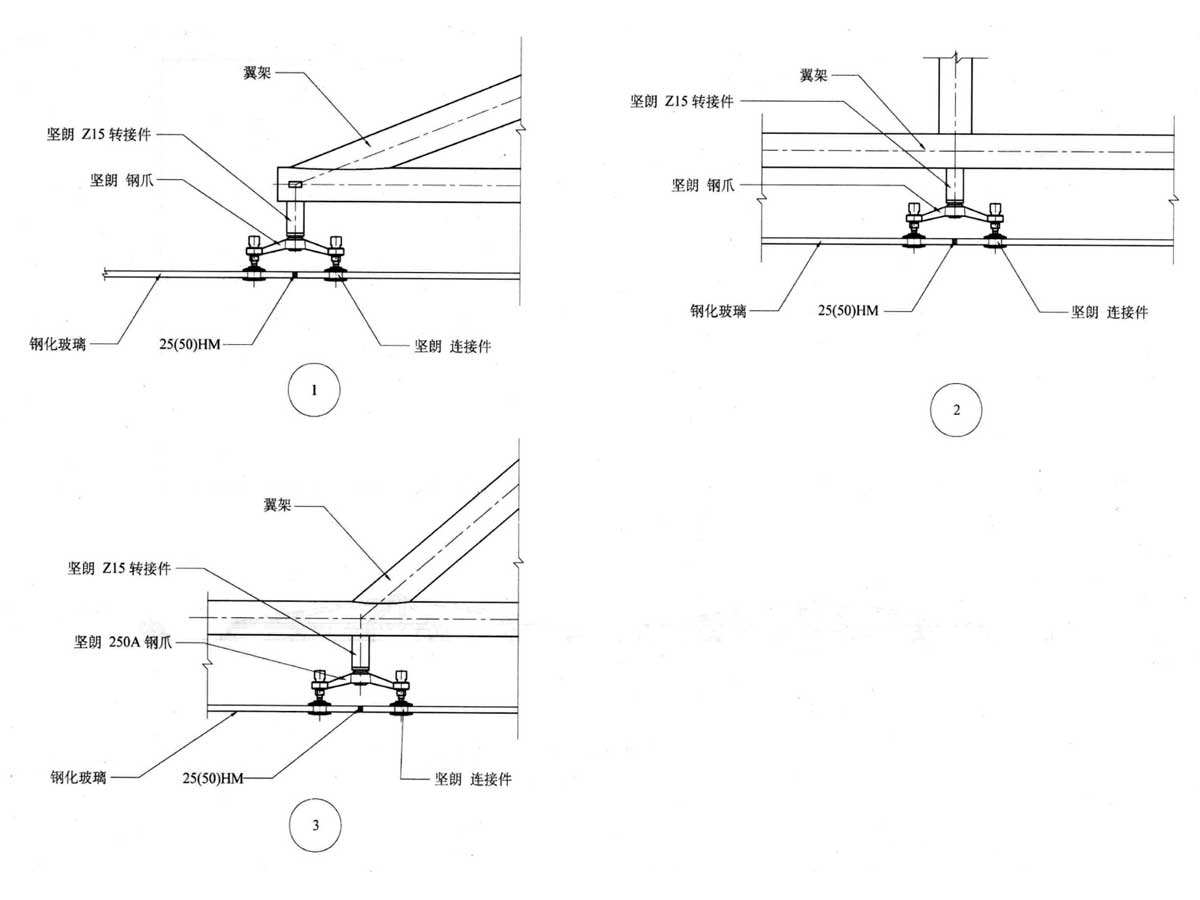
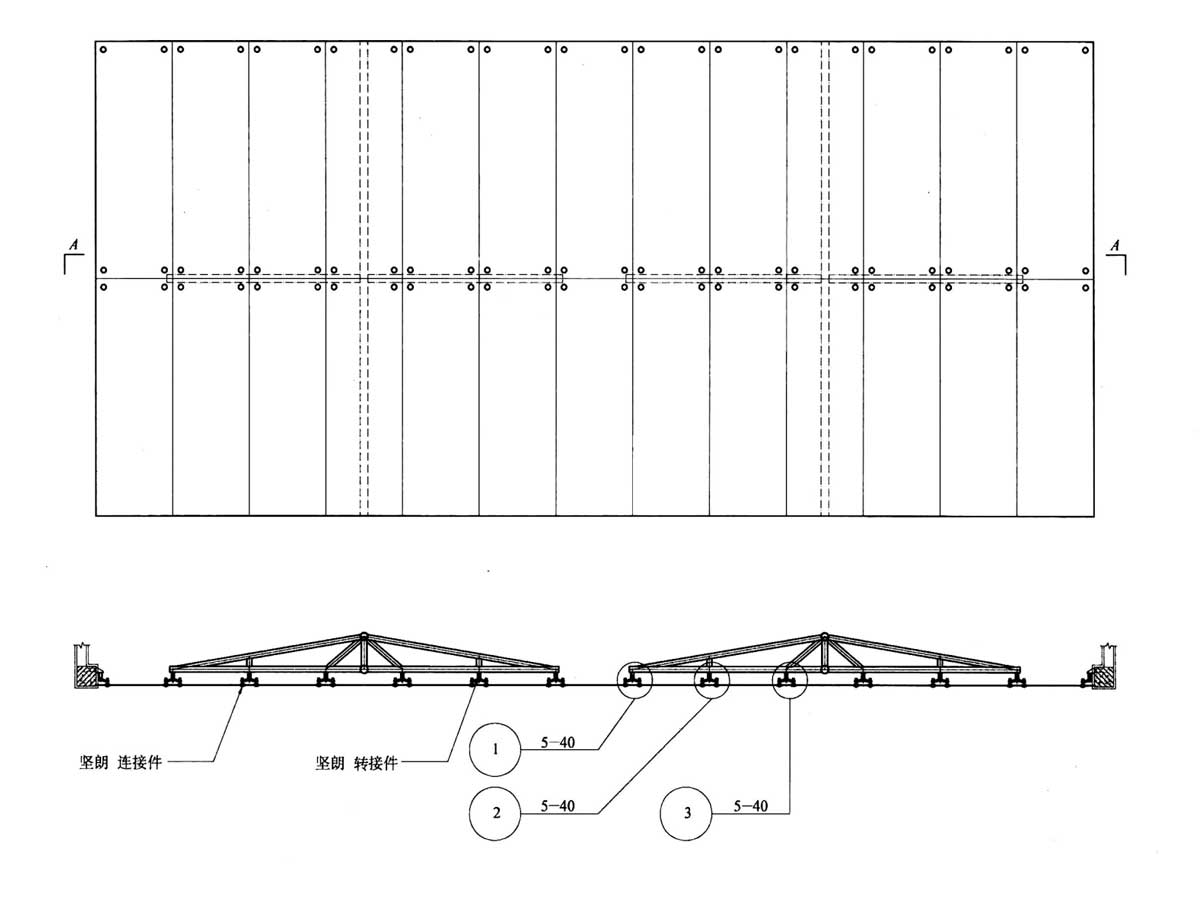
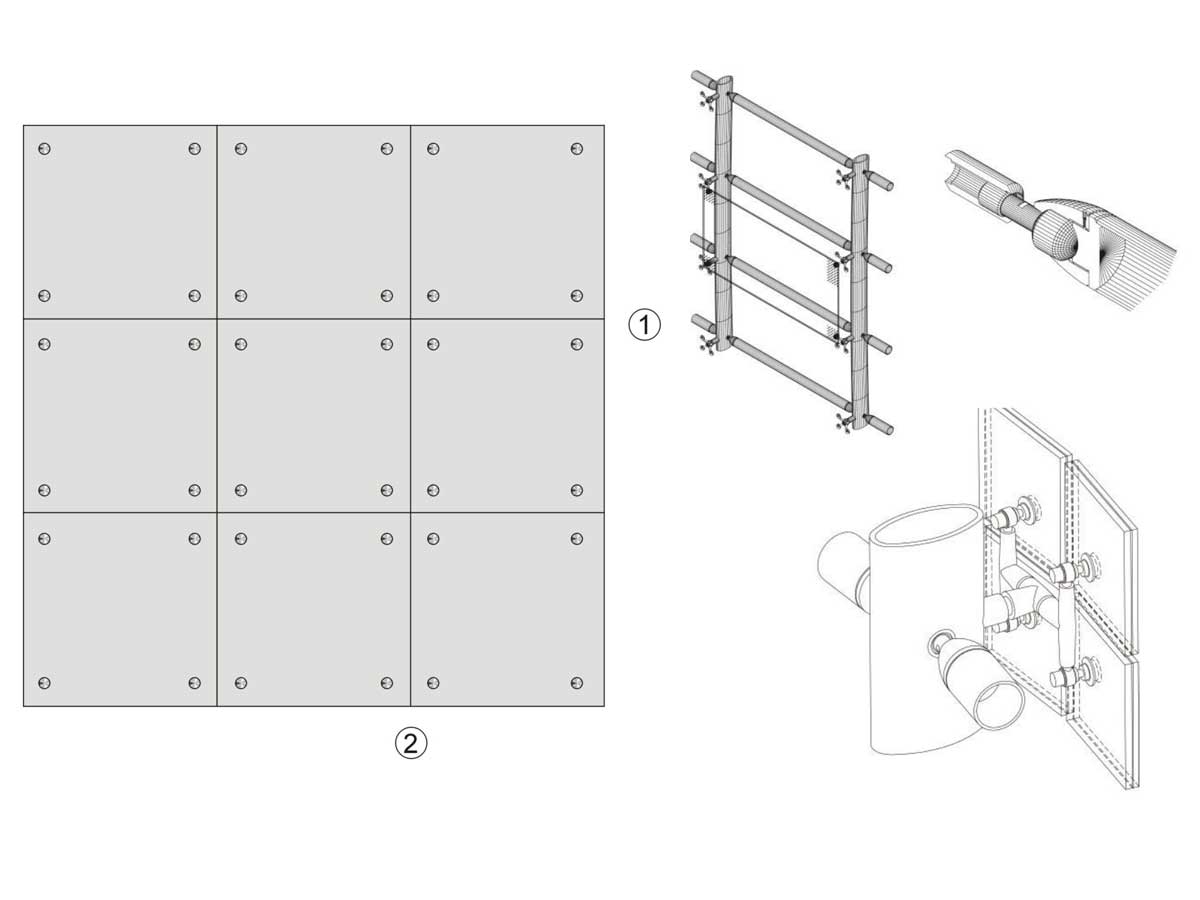

Types of Glass Curtain Walls
- Stick-Built Curtain Walls:
- Components of the curtain wall (framing, glass, and other elements) are delivered to the construction site in individual pieces and assembled piece-by-piece.
- Advantages: Flexibility for complex designs and custom detailing. Ideal for projects where materials need to be customized or adapted on-site.
- Disadvantages: Longer installation time and more labor-intensive.
- Unitized Curtain Walls:
- Pre-fabricated in sections (or “units”) in a factory and then transported to the site for installation as large panels.
- Advantages: Faster installation, higher precision, and reduced on-site labor costs.
- Disadvantages: Limited flexibility once sections are prefabricated.
- Structural Glazing Curtain Walls:
- Uses a special adhesive system to attach the glass directly to the frame, without the need for visible framing members.
- Advantages: Cleaner aesthetic with minimal framing visible, offering a sleek and modern appearance.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and complex installation process
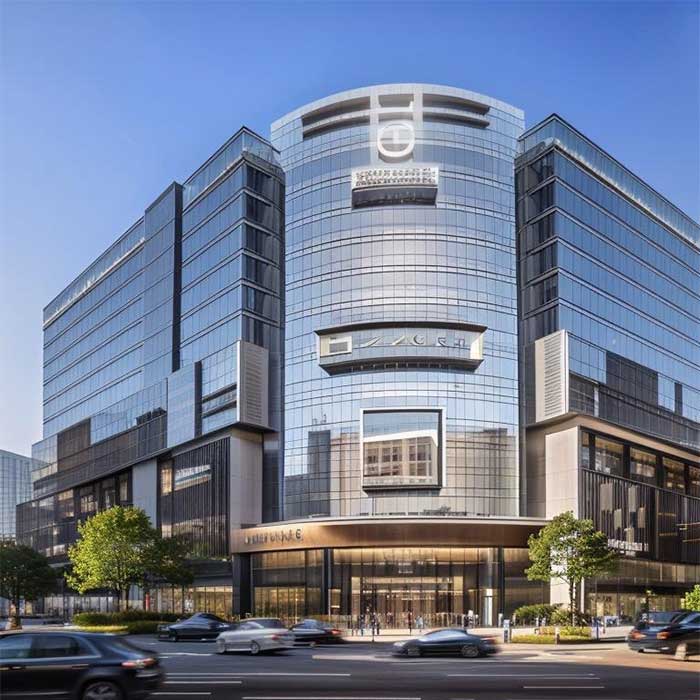
Common Applications of Glass Curtain Walls
- Commercial Buildings:
- Used extensively in office buildings, malls, and public spaces. The transparency of the glass maximizes the view, provides natural light, and enhances the appearance of the building. High-performance glazing is often incorporated for energy efficiency.
- Residential Buildings:
- High-end luxury residential projects often incorporate glass curtain walls to create dramatic views, enhance daylighting, and offer a modern architectural style.
- Transportation Hubs:
- Airports, train stations, and bus terminals often use large glass curtain walls to provide open, spacious environments, while still protecting the interior from weather and reducing noise.
- Mixed-Use Developments:
- For large-scale urban projects, glass curtain walls can be used to connect residential, retail, and office spaces, creating a cohesive design and allowing natural light to flow through the complex.
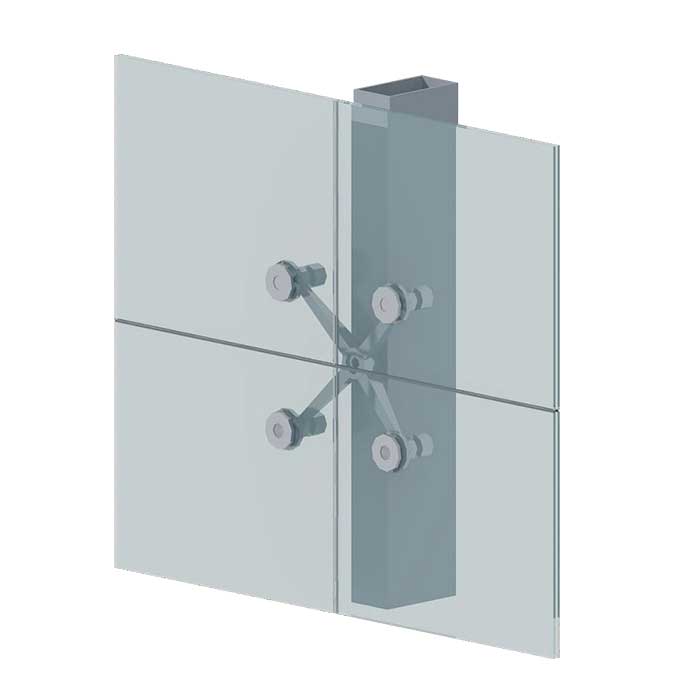

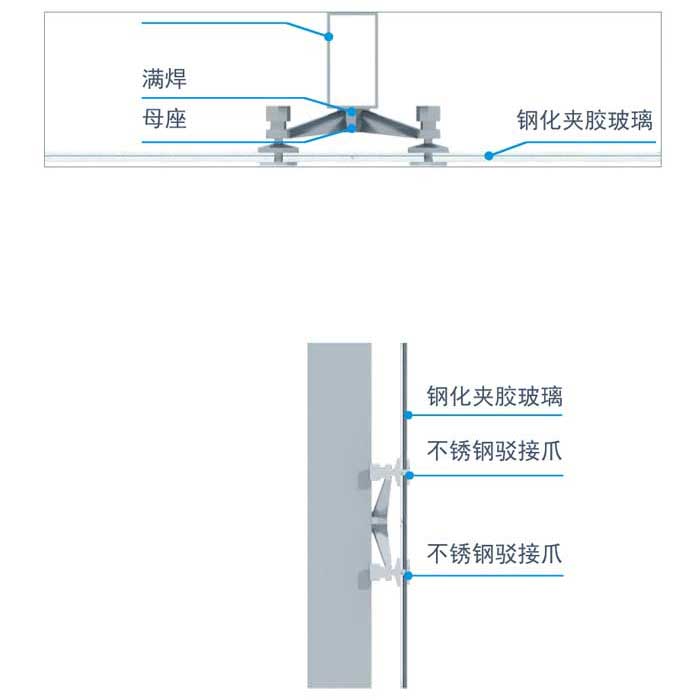





评价
目前还没有评价